Plate Heat Exchanger Gasket

| Seal Material | Temperature | Suitable for fluid |
| NBR | -15C°to +130C° | Water, seawater, mineral oil brine |
| NHNBR | -15C°to +160C° | High temperature mineral oil, high temperature water |
| EPDM | -25C°to +180C° | Hot water, steam, acid, alkali |
| Viton/FKM | -5C°to +180C° | Acid, alkali, fluid |
Plate Heat Exchanger Plate
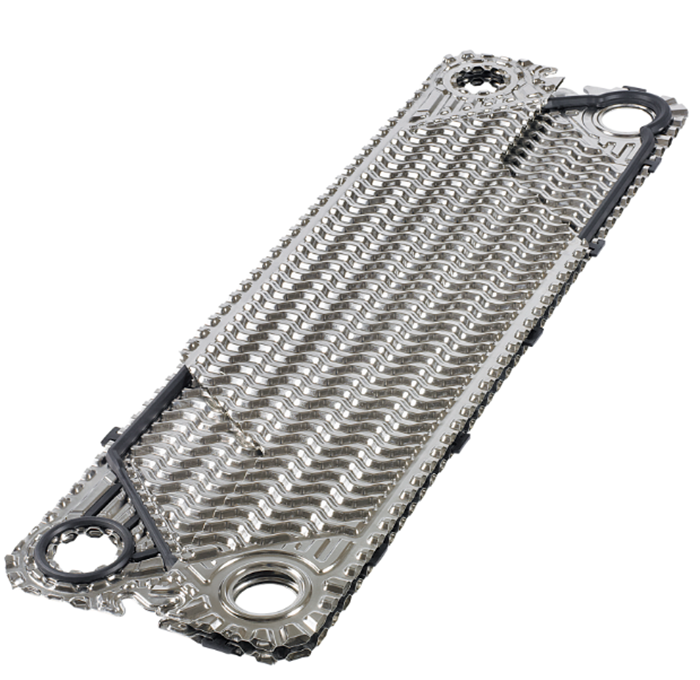

| Plate Material | Suitable for fluid |
| Stainless steel (Alloy304, Alloy 316) | Clean water, river water, edible oil, mineral oil |
| Titanium and titanium palladium (Ti) | Sea water, salt water, salt |
| 20Cr, 18Ni, 6Mo (254SM0) | Dilute sulfuric acid, sparse salt solution, inorganic solution |
| Nickel (Ni) | High temperature, high concentration caustic soda |
| HASTELLOY alloy (C276, D205, B2G) | Concentrated sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, phosphoric acid |
| Graphite |
Hydrochloric acid, medium concentration sulfuric acid, phosphoric acid, hydrofluoric acid |
Plate Heat Exchanger
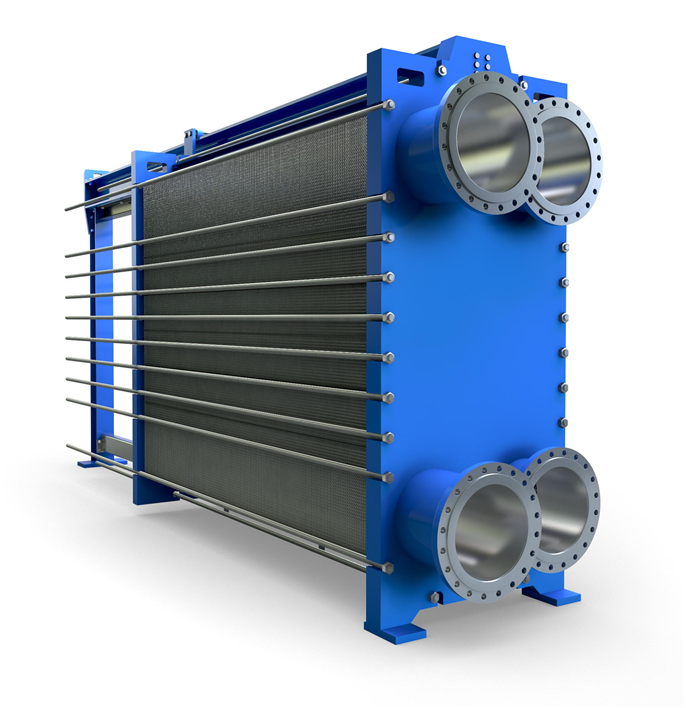
Plate Heat Exchanger Rubber Liner & Collar
Plate heat exchangers consist of relatively few parts. Because plate heat exchangers are used for transferring heat, they require inlets and outlets where the flowing mediums -or fluids– can enter and leave the heat exchanger. A fluid may be a liquid or a gas. As fluids are often assumed to be liquid only, we will use the term flowing medium to avoid confusion.
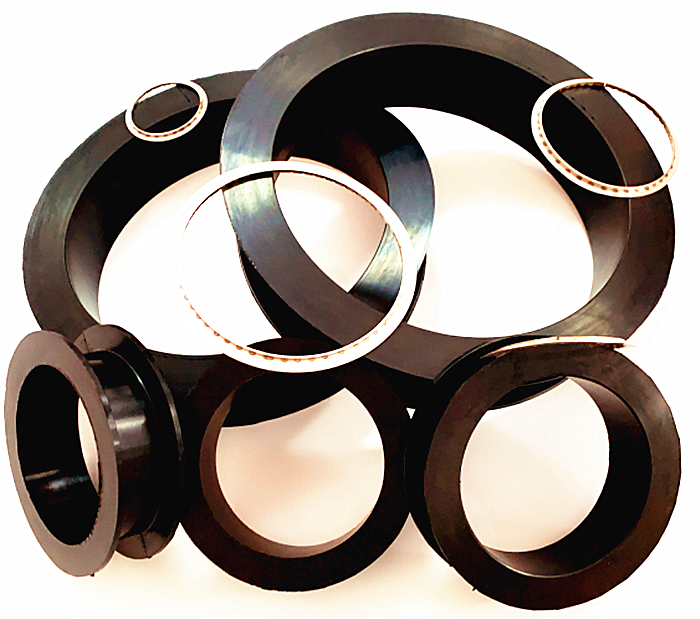

| Rubber Liner | Flu rubber | EPDM | NBR |
|
Tensile Strength Mpa |
≥13 |
≥16 |
≥17 |
| Elongation % |
≥120 |
≥170 |
≥200 |
| Shore A Hardness | 80±5 | 80±5 | 75±3 |
| Tear Strength KNM |
≦30 |
≦30 |
≦30 |
| Compressive Deformation | 24h*23≦2.5 |
24h*23≦5 |
24h*23≦2.5 |
| 24h*180≦15 | 24h*150≦15 | 24h*125≦15 | |
| Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
